Endoplasmic reticulum: Endoplasmic reticulum, continuous membrane system within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and that serves multiple functions.
How much protein can you eat on the ketogenic diet is a question asked by many when they realize protein intake is just as important as cutting the carbs.
Creating Glucose. Carbohydrates consist of molecules of sugar, which your body digests into glucose and uses for energy. When you’re short on carbs, glucose can be created from fat and protein in a process called gluconeogenesis.
One of the well-known mantras of the ketogenic diet is very low carb intake and high fat intake. But there’s another nutrient that’s important to monitor when going keto—and a lot of people make the mistake of not considering its importance.
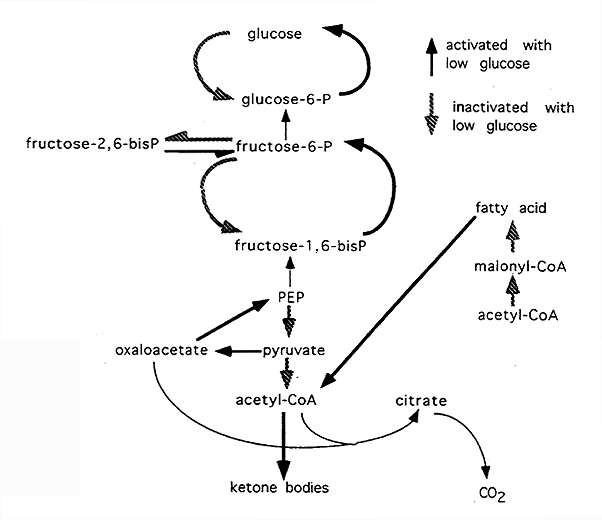

If there’s no more glucose or glycogen to be had, a process called gluconeogenesis begins in the liver (“gluco” = glucose, “neo” = new, “genesis” = to make).
Recently (for some conception of recent) we asked the question: If You Eat Excess Protein, Does It Turn Into Excess Glucose? One of the potentially confusing aspects of this question, is the difference between gluconeogenesis (GNG) — the creation of new glucose that didn’t exist before, and
The Medical Biochemistry Page is a portal for the understanding of biochemical, metabolic, and physiological processes with an emphasis on medical relevance

### Gluconeogenesis Diabetes ★★ Diabetes Cure Found In Utah The 3 Step Trick that Reverses Diabetes Permanently in As Little as 11 Days.[ GLUCONEOGENESIS DIABETES ] The REAL cause of Diabetes ( Recommended )

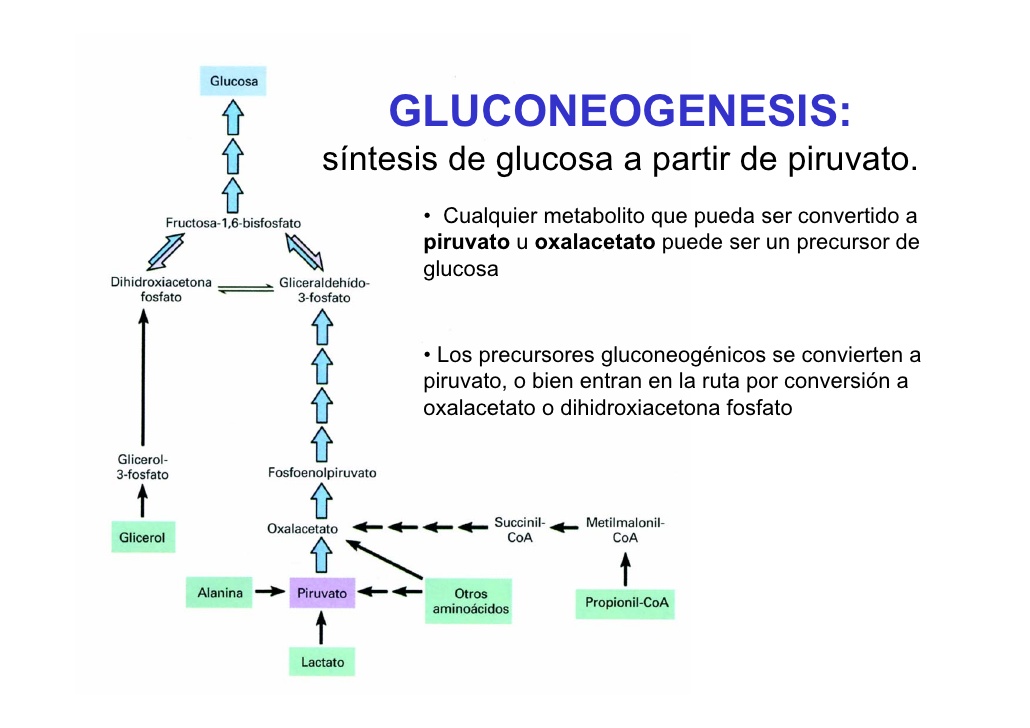

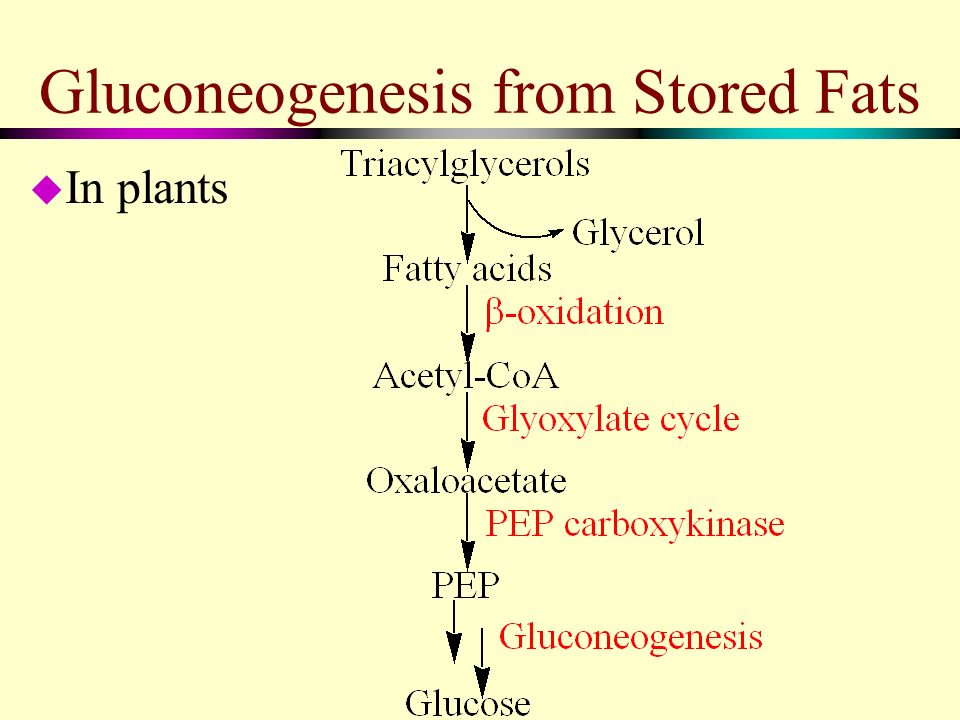
Gluconeogenesis: definition, pathway, steps, precursors. Where and when it occurs. Reactions, enzymes, energy cost, coordinated regulation with glycolysis.

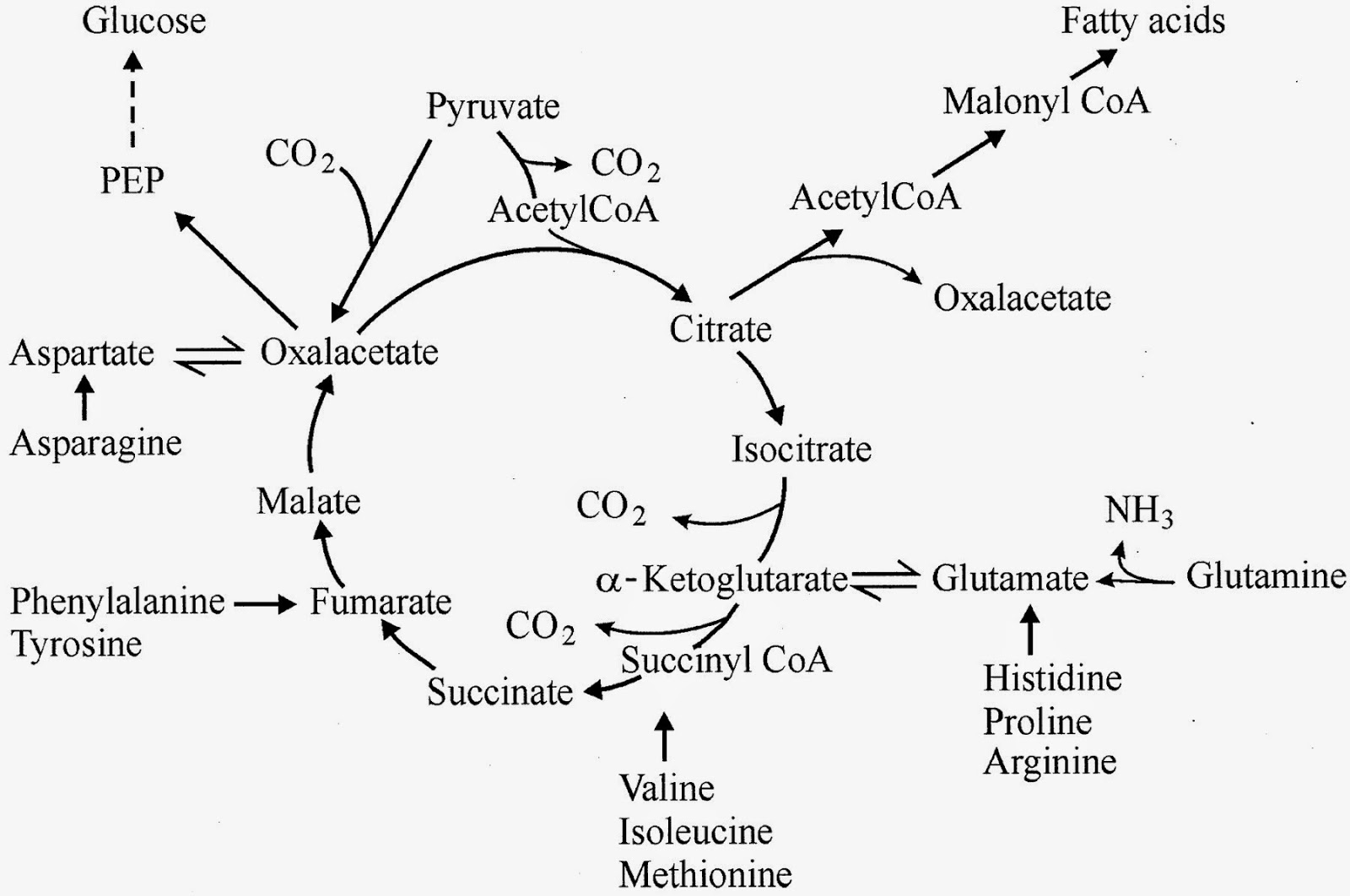
I remember the first time I came across the “cortisol” argument. It took me about five minutes to find a couple of online biochem textbooks that said, “gluconeogenesis is activated by glucagon”.